EV Charger Installation at Home: What to Know Before You Plug In
January 29, 2026

As electric vehicles (EVs) rapidly become a mainstream choice for environmentally conscious drivers, the need for convenient home charging solutions has never been greater. Installing an EV charger at home offers unparalleled convenience, allowing you to charge your vehicle overnight without relying on public stations. However, not all installations are created equal, and a successful setup requires careful planning, professional insight, and an understanding of the technical and regulatory requirements involved. For homeowners, awareness of these factors ensures safety, efficiency, and long-term cost savings.
The EV market in the United States is expanding at an unprecedented rate, driven by government incentives, evolving technology, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. Understanding these factors before you plug in your vehicle is essential to avoid hazards, reduce costs, and ensure reliable daily use. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of what homeowners need to know before installing an EV charger at home, from technical requirements to real-world insights, enabling confident decisions for a seamless charging experience.
Understanding EV Charger Types and Power Levels
Level 1 Chargers: The Basic Option
Level 1 chargers are the simplest and most widely compatible option for home use. They typically operate using a standard 120-volt household outlet, delivering a slow charge of about 3–5 miles of range per hour. Level 1 chargers are ideal for homeowners with short commutes or those who can leave their EV plugged in for extended periods. The main advantage is minimal upfront cost, as most vehicles come with a portable Level 1 charger. However, the slow charging rate may be inconvenient for larger battery packs or households with multiple EVs.
Practical Scenario:
A commuter who drives 30 miles daily can fully recharge their EV overnight with a Level 1 charger. For households with higher daily mileage, this setup may not provide sufficient range without careful planning.
Level 2 Chargers: Fast and Efficient Charging
Level 2 chargers operate on a 240-volt circuit and deliver significantly faster charging, providing 15–30 miles of range per hour. These chargers are ideal for homeowners looking for efficiency, particularly for larger vehicles or families with multiple EVs. Installation requires a dedicated circuit, professional wiring, and sometimes an electrical panel upgrade to accommodate the additional load.
Benefits: Level 2 chargers reduce the time needed to recharge an EV, allowing drivers to maintain flexibility and independence. They also support smart features like scheduled charging and energy monitoring, offering cost savings when paired with off-peak electricity rates.
Expert Insight: Choosing the right Level 2 charger depends on your EV’s onboard charger capacity and your typical driving patterns. Professional installation ensures that your electrical system can handle the load safely and efficiently.
DC Fast Chargers: Commercial-Grade Speed at Home?
While DC fast chargers offer the quickest charging speeds, they are typically reserved for commercial applications due to their high cost and substantial electrical requirements. Most residential setups do not support these chargers without major electrical upgrades, making them impractical for typical homeowners. However, understanding their existence is useful for planning future-proof installations.
Electrical Considerations for Home Installation
Assessing Your Home’s Electrical Capacityc
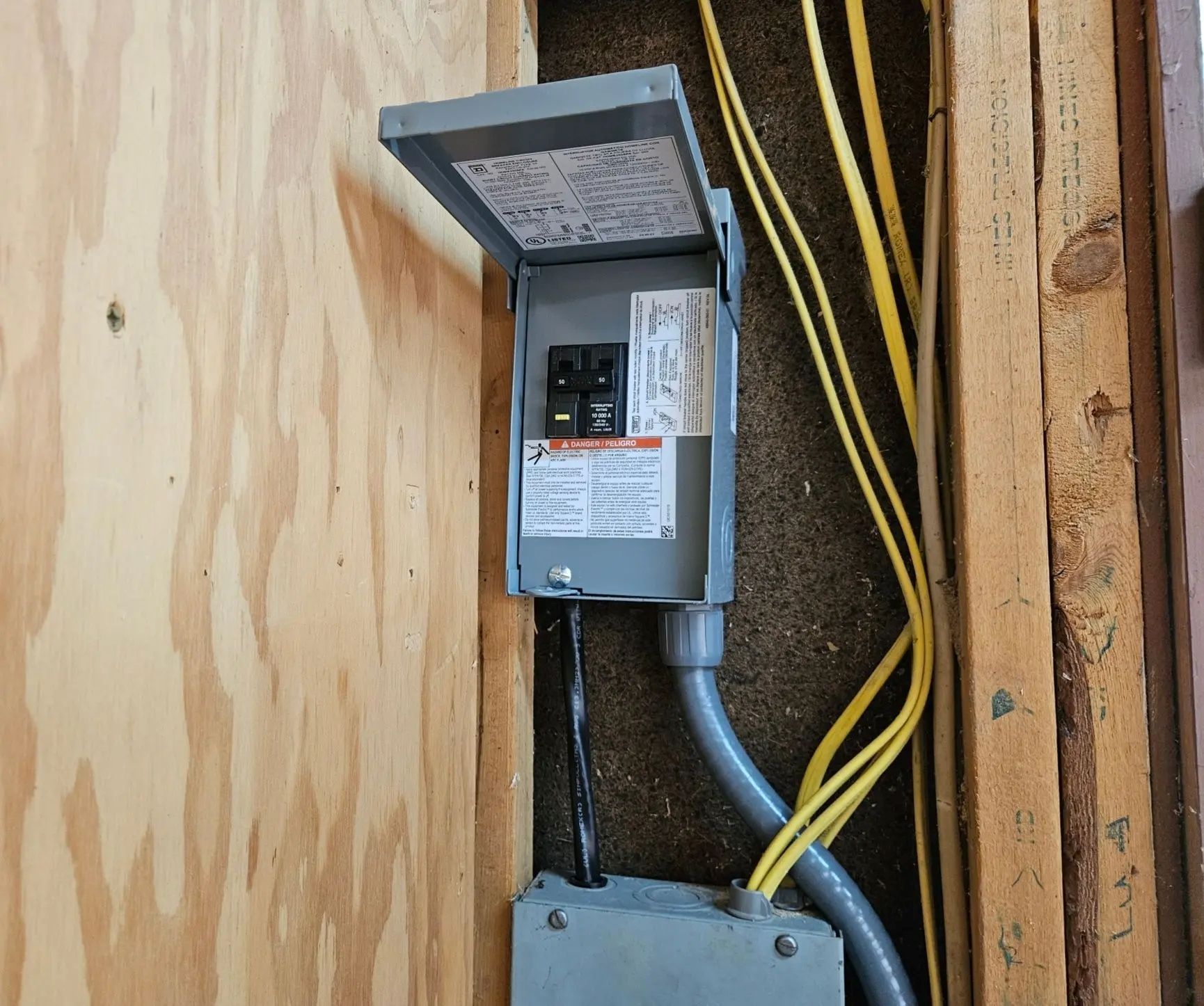
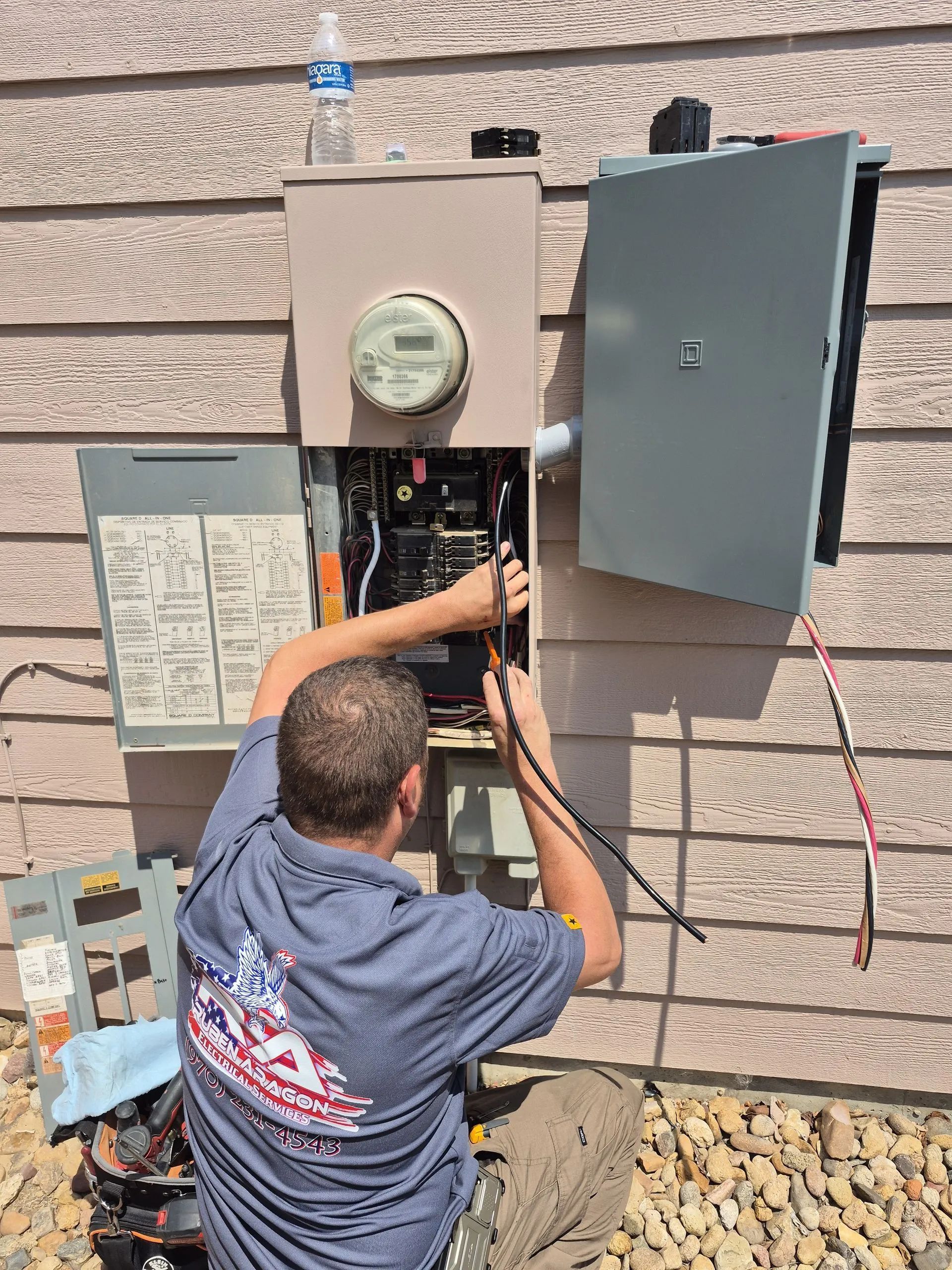
Before installing any EV charger, it is crucial to evaluate your home’s existing electrical system. A typical single-family home may have a 100–200 amp service panel, and adding a Level 2 charger could require 30–50 amps, depending on the charger’s specifications. Older homes may need panel upgrades to accommodate this additional load safely.
Tip: Engage a licensed electrician to assess your panel, breakers, and wiring. Attempting to install a high-capacity charger without proper upgrades can lead to overheating, fire hazards, and code violations.
Circuit Requirements and Safety Protocols
EV chargers require dedicated circuits to operate efficiently and safely. For Level 2 chargers, this usually means installing a new 240-volt circuit with an appropriately rated breaker. Grounding and proper wire sizing are critical to prevent electrical faults. Safety features such as circuit breakers, surge protectors, and GFCI protection may also be required depending on local building codes.
Real-World Example: A homeowner installing a 40-amp Level 2 charger in a home with a 100-amp service panel may need to upgrade to a 200-amp panel to safely support the additional load without overtaxing the system.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Planning
Home EV charging can significantly impact your electricity bills if not managed efficiently. Smart chargers that allow for off-peak charging schedules can reduce costs by leveraging lower electricity rates during nighttime hours. Additionally, integrating solar panels or home energy management systems can further optimize costs and reduce reliance on the grid.
Location and Installation Logistics
Choosing the Optimal Charger Location
Installation Challenges in Different Home Layouts
Not all homes have the ideal layout for a straightforward installation. Long cable runs, detached garages, or complicated panel access may require additional labor and materials. Homeowners with challenging setups should anticipate higher installation costs and consider conduit placement, trenching, or wiring modifications.
Expert Advice: Early consultation with a licensed electrician helps identify potential obstacles and ensures a smoother installation process, avoiding unnecessary delays and cost overruns.
Costs and Incentives for Home EV Chargers
Installation Costs
The cost of a home EV charger can vary widely based on the charger type, electrical upgrades, and labor requirements. Level 1 chargers are relatively inexpensive, often included with the vehicle, while Level 2 chargers can range from $400 to $1,500. Installation may add $500–$2,500, depending on the complexity of electrical work and required permits.
Example: A simple Level 2 installation in a modern home with a robust panel may cost around $1,000, whereas a complex installation requiring a panel upgrade and extensive wiring could exceed $3,500.
Tax Credits and Incentives
Federal, state, and utility incentives can significantly offset the cost of home EV chargers. For instance, the U.S. federal government currently offers tax credits covering a percentage of both the hardware and installation costs. Local utility companies may provide rebates or discounted rates for EV charging during off-peak hours.
Tip: Research available incentives before installation to maximize savings. Combining multiple incentives can reduce the overall out-of-pocket expense, making home charging more accessible and affordable.
Smart Charging and Future-Proofing
Smart Charger Features
Modern EV chargers often include smart features, such as Wi-Fi connectivity, app controls, energy monitoring, and scheduling capabilities. These features allow homeowners to optimize charging based on electricity rates, track energy usage, and even integrate with renewable energy systems like solar panels.
Benefit:
Smart chargers enhance convenience, save money, and reduce the environmental impact of home EV charging. They can also be updated remotely, ensuring compatibility with future EV models.
Planning for Multiple Vehicles
As EV adoption grows, some households may own multiple electric vehicles. Planning for future expansion involves choosing chargers with higher amperage capacity, installing multiple circuits, or selecting units that can share power intelligently between vehicles.
Scenario:
A family with two EVs may install a dual-port charger with load-balancing capability, ensuring that both vehicles charge efficiently without overloading the electrical system.
Common Challenges and Expert Tips
Managing Electrical Load
One of the most common challenges in home EV charger installation is managing electrical load without straining the home’s system. Professional electricians recommend conducting a load calculation before installation to prevent tripped breakers, reduced charging efficiency, or potential hazards.
Navigating Permits and Codes
Local building codes and permitting requirements vary by municipality. Many jurisdictions require permits for EV charger installations, particularly for Level 2 chargers. Noncompliance can lead to fines, failed inspections, or unsafe installations.
Tip: Hire a licensed professional familiar with local regulations to ensure compliance. They can handle permitting, inspections, and documentation, streamlining the process for homeowners.
Ensuring Long-Term Safety
Proper installation is critical for long-term safety. Using high-quality chargers, ensuring correct grounding, and scheduling periodic inspections can prevent electrical failures and extend the life of the charging system.
Expert Insight: Routine maintenance, including visual inspections and professional checks every few years, helps identify wear, corrosion, or loose connections before they become serious issues.
Dependable Solutions from Local EV Charging Professionals
Installing an EV charger at home offers convenience, efficiency, and the freedom to embrace sustainable transportation without relying solely on public infrastructure. From understanding charger types and electrical requirements to navigating installation logistics and incentives, homeowners must approach the process with careful planning and expert guidance. By evaluating your electrical system, selecting the appropriate charger, and following best practices, you can ensure a safe, reliable, and cost-effective charging solution that meets your daily needs. Smart chargers and future-proofing strategies further enhance convenience and energy efficiency, preparing your home for the evolving landscape of electric mobility.
For homeowners in Greeley, Colorado seeking
professional EV charger installation, Ruben Aragon Electrical Services LLC
brings over 20
years of experience delivering reliable, safe, and efficient electrical solutions. Our team specializes in residential EV charger setups, electrical panel upgrades, and comprehensive system assessments. Trust our professionals to guide you through every step, from planning and permitting to installation and maintenance, making home EV charging simple, safe, and efficient.

Share this article

